When spring is in the air in Japan and iron storm by Russia were starting to cover Ukraine, the author has released several articles, basing on genetics papers which indicate the ineffable unusual genetlc structure of Korean gene. It is at the heart of genetic research for an isolated and homogeneous ethnic population that analyzing of inherent mutation and the frequency of the gene provides more information for promoting mental and physical health of the population. I strongly feel that The Koreans need "gene therapy", but it is needless to say that it absolutely is impossible to do comprehensive "gene therapy" for humans except for rare genetic disease even in the breakthroughs of modern genetic technology. Although hard as contents of this article are to comprehend, it is no coincidence that there are various "insane things" at Korean Peninsula and genetics paper which indicates the peculiarity of Korean DNA
 Korean actress. There are no Korean women who won
international beauty pageants in the past ten years.
Korean actress. There are no Korean women who won
international beauty pageants in the past ten years.
We, humans around the world, should know the fact that The Koreans carry strange genetic architecture.
 Please strongly keep in your mind that the following
citation from population genetics paper clearly indicate
peculiarity of The Koreans DNA.
Please strongly keep in your mind that the following
citation from population genetics paper clearly indicate
peculiarity of The Koreans DNA.Based on our analysis, we hypothesize that Koreans might have different responses to the above mentioned terms-related drugs, when compared to other populations.
Therefore, we rationally conjectured that Korean only SNVs prevalent across many of the individuals would be more important for treating Koreans differently from other populations in the personalized medicine.
Therefore, we inferred that special attention should be made for the Korean population when treated for the above mentioned terms related diseases, since other populations did not carry those Korean only SNVs.
United States Department of State do make a warning to young women's journeys to South Korea about sexual assault. Please strongly note that the United States don't make same warning to other countries (i.e. China, Japan etc.)
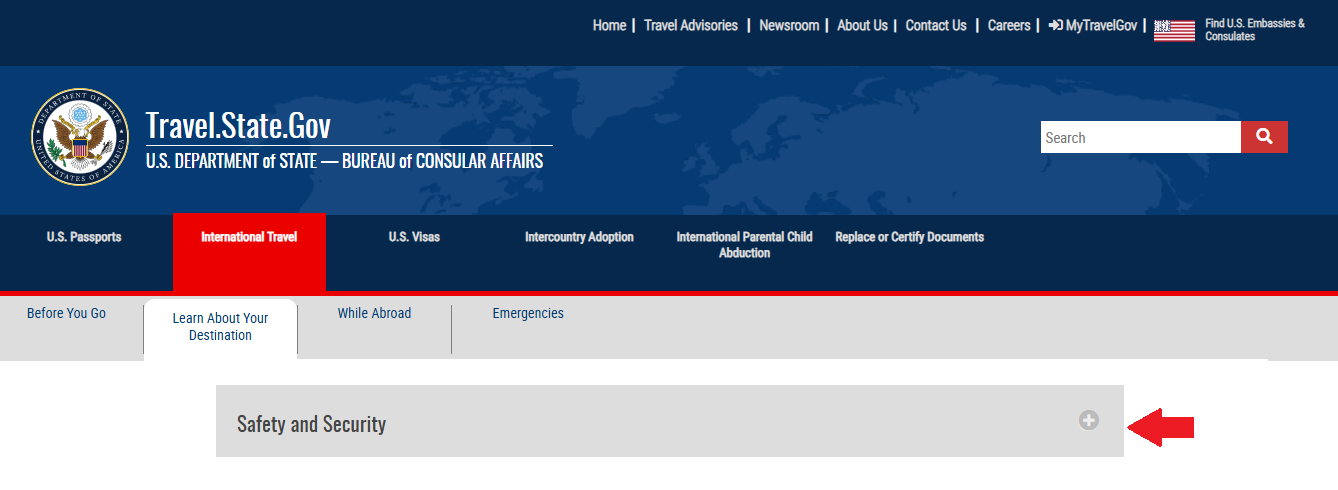
Sexual Assault: The Embassy regularly receives reports of sexual assault from U.S. citizens. Most cases involved young women assaulted by acquaintances they met on social media, dating, or messaging apps. Alcohol is often involved, and Korea’s low overall crime can create a false sense of security. Specialized hospital units and police are available in South Korea to assist victims, however services in English and responsiveness to the crime are not always consistent. In general, sex crimes are not punished as harshly in South Korea as in the United States and the road to prosecution is a challenging one for victims.
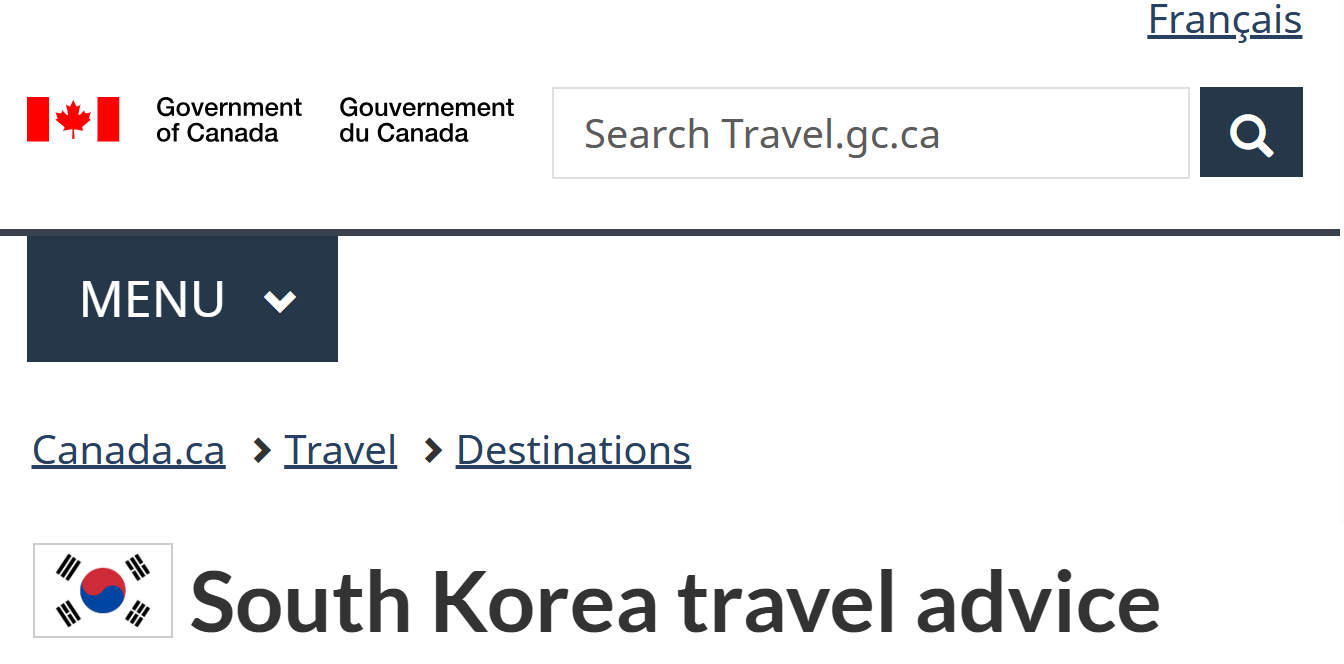
Women’s safety
Women travelling alone may be subject to certain forms of harassment. Sexual assault and harassment do occur, particularly around bars and nightlife areas, such as Itaewon and Hongdae-Ipgu.
Local authorities may not always respond adequately to reports of sexual violence and harassment. If you are sexually assaulted, you should report it immediately to local authorities and to the nearest Canadian government office.
- Avoid travelling alone, especially at night
- Remain vigilant
- Be careful when dealing with strangers or recent acquaintances
What is "family-destroying criminals"?
The Korean "Comfort Women": Movement for RedressChunghee Sarah Soh
Dec 1996
In resent years, young male criminals in South Korea take advantage of this traditional view by raping women in front of members of their families in order to ensure that robbery would not be reported to police. The media refers to these raping robbers as "family destroying criminals" because of the shattering impact of their behavior on the viability of the family; the raped woman is now sullied in the eye of her husband, herself, and other members of the family, which may eventually break up under the psychological strain.
Historical facts
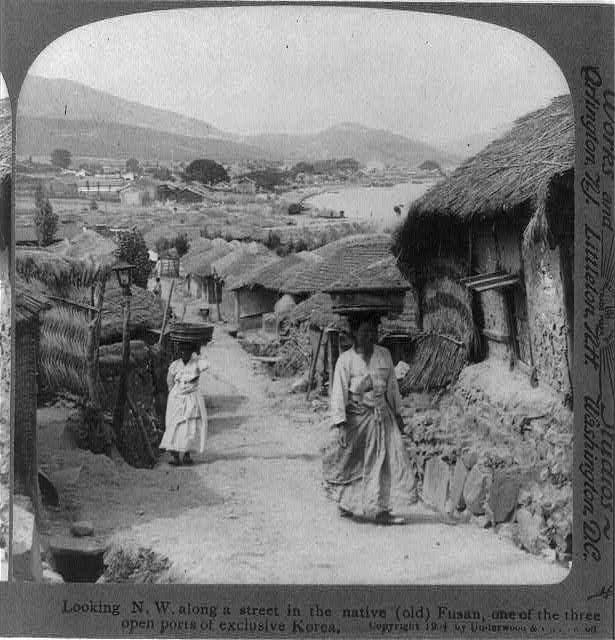

Looking N.W. along a street in the native (old) Pusan, Korea 1904 year
Image source: Library of Congress in United States

Image source:London, Jack, 1904-1905

image source:London, Jack, 1904-1905
[notes]
Even in the black and white image, you can see that the clothing is all white.
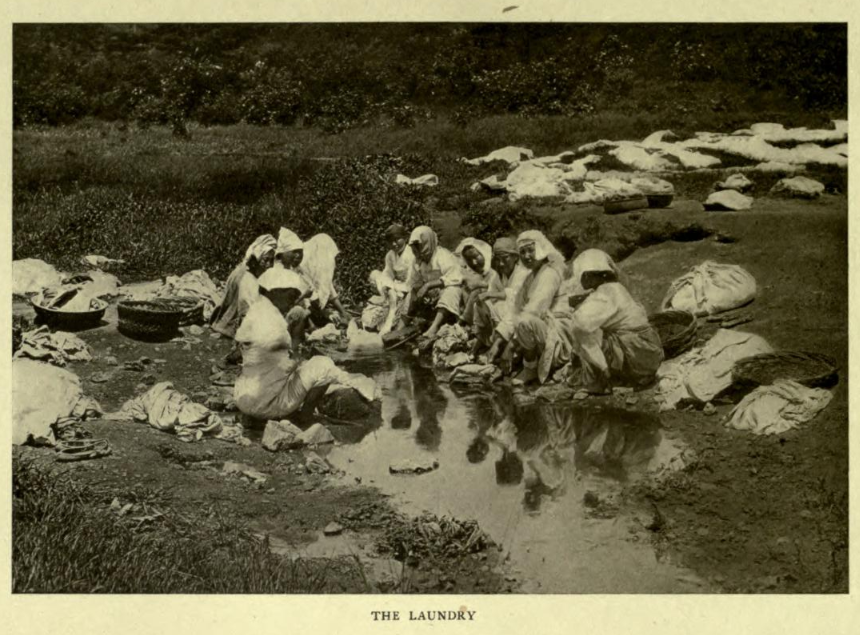

The Laundry
image source:The passing of Korea, Homer B. Hulbert 1906

A Korean Village
Image source: Fifteen Years Among the Top-Knots; Or, Life in Korea published in 1904
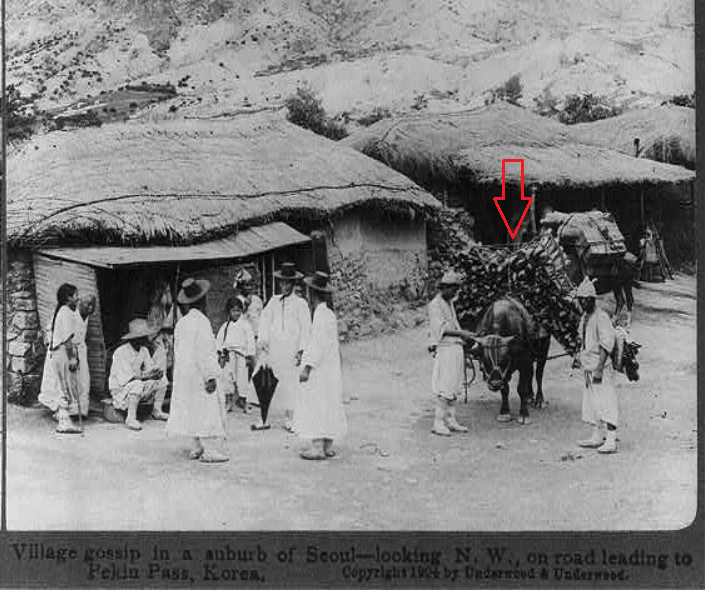

Village gossip in a suburb of Seoul - looking N.W., on road leading to Pekin Pass, Korea,1904
Image source: Library of Congress in United States
[Notes]
The red arrow is not in the original image, but was added by the author of this article.
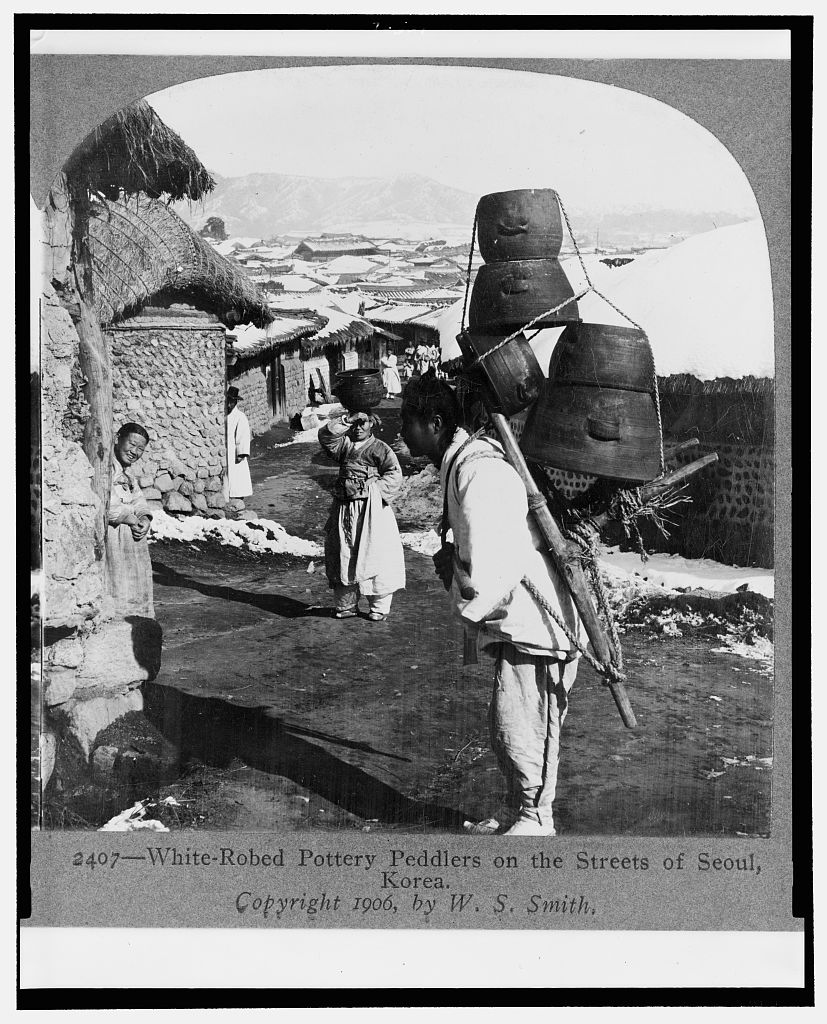

White-robed pottery peddlers on the streets of Seoul, Korea 1906 year
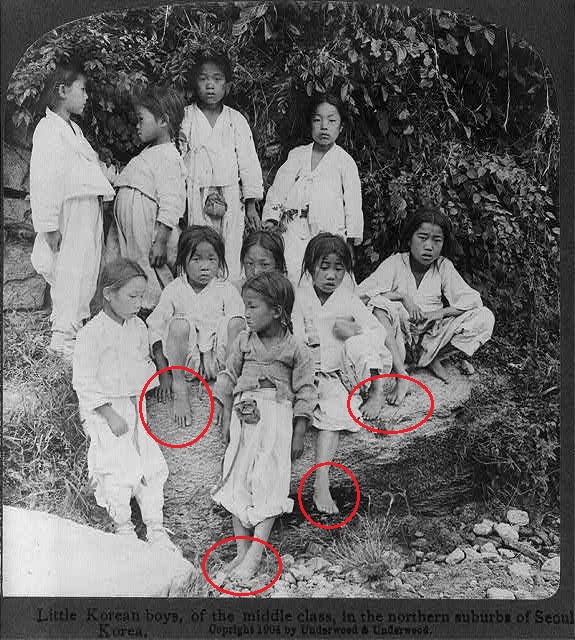

Little Korean girls, of the middle class, in the northern suburbs of Seoul, Korea 1904 year
Image source: Library of Congress in United States
[Notes]
The red circle is not in the original image, but was added by the author of this article.
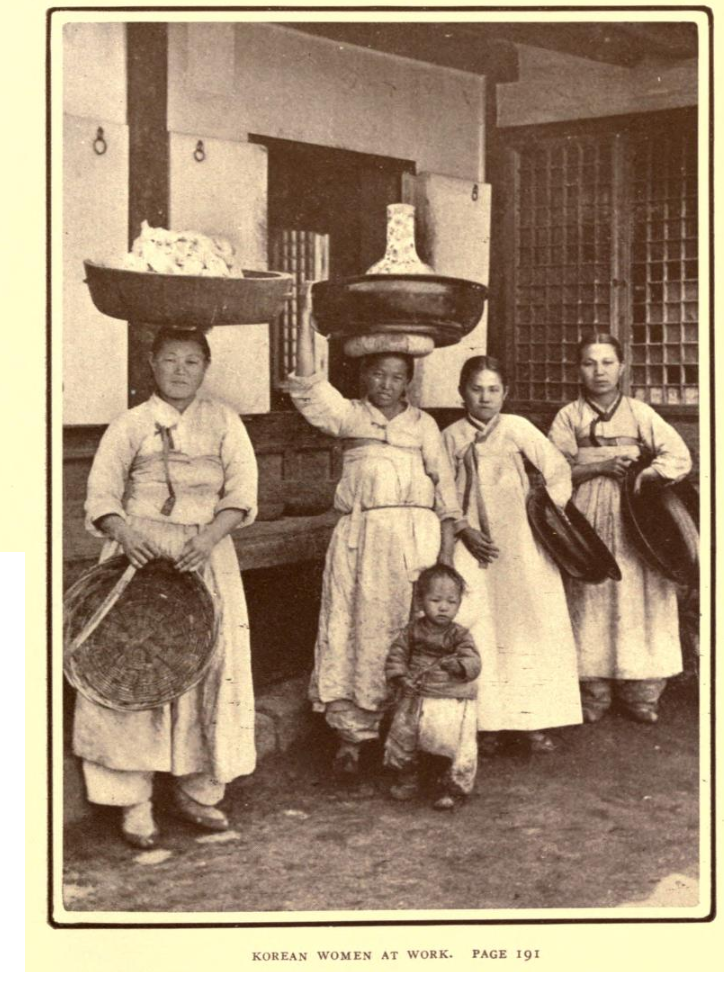

Korean Women at work
Image source: Fifteen Years Among the Top-Knots; Or, Life in Korea published in 1904
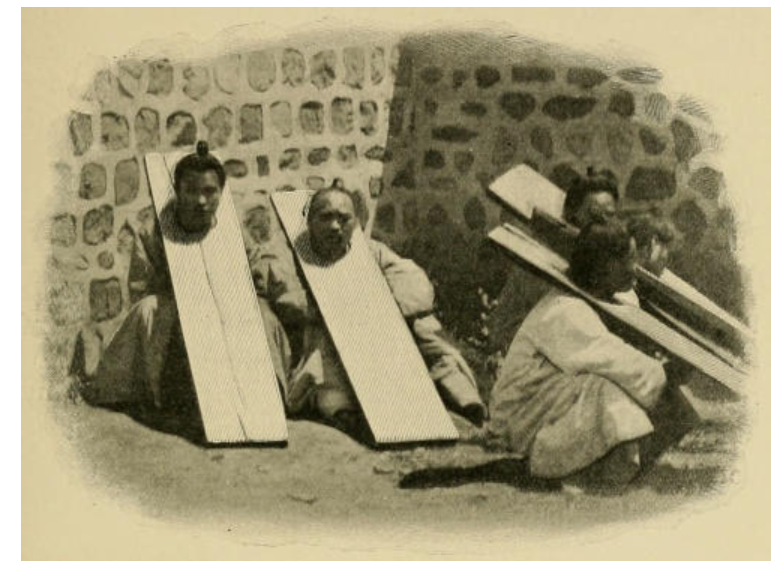
Justice is not tempered with mercy
image source: KOREA BY ANGUS HAMILTON 1904
[notes]
This photo shows the punishment for criminals.

Published. 1892, photographer name:Buichi Hayashi, Northwest entrance gate to Seoul, Korea
image source:National Diet Library in Japan

Natives praying to wooden devils, Chosen(Korea),1919
Image source: Library of Congress in United States
South Korea
It astonishingly is the most absurd lie


North Korea
It might be the worst place on the earth?
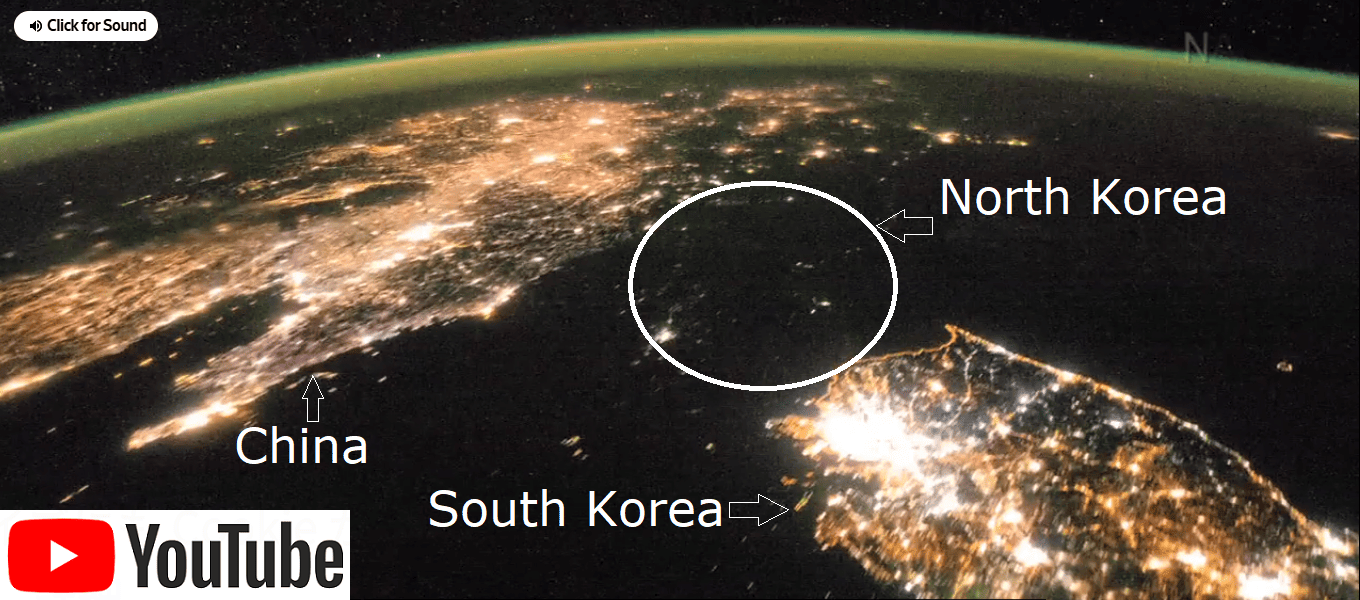
 From NASA images. The image symbolize North Korea=Kim dynasty.
From NASA images. The image symbolize North Korea=Kim dynasty. The image above links to a French tourist's video
(YouTube) of North Korea in 2010.
The image above links to a French tourist's video
(YouTube) of North Korea in 2010.
 This video was filmed in 2010
by AsiaPress which is press website in Japan of information of North Korea.
This video was filmed in 2010
by AsiaPress which is press website in Japan of information of North Korea.Strange phenomenon in South Korea
Total fertility rate in South Korea is abnormal !
 Although it's
a conundrum that why South Korea women don't want to have children,
there could be no dispute that only competition in university entrance
exam is fair competition in South Korea. Therefore, they must spend huge
money to "cram school" for enrolling into prestigious university, and pupils in high
school are forced to learn for long hours at high school and "cram
school" every day, so high expenses for preparing for university entrance exams may be the reason for extreme low fertility rate in South Korea. In other word, the source
of low birth rate is competitive personality among The Koreans.
Although it's
a conundrum that why South Korea women don't want to have children,
there could be no dispute that only competition in university entrance
exam is fair competition in South Korea. Therefore, they must spend huge
money to "cram school" for enrolling into prestigious university, and pupils in high
school are forced to learn for long hours at high school and "cram
school" every day, so high expenses for preparing for university entrance exams may be the reason for extreme low fertility rate in South Korea. In other word, the source
of low birth rate is competitive personality among The Koreans.Korean Actress. Please notice that Korean women have "same jawline" as the result of cosmetic surgery.

Suicide rates is the highest in the world
 A great majority of researchers in South Korea make a pretext of that old Koreans indicates high suicide rate compared with adolescents
as for why suicide rate in South Korea is the highest in the world.However, in part due to deliberately focus on suicide rate, i think that the essence that Koreans carry inherent variants
of MDD(major depressive disease) deliberately have been overlooked.
It is
a complete and scientific fact and is beyond all doubts that the Koreans carry numerous brain-related variants inherent to the Koreans which might be the cause of
The Koreans specific mental disorder i.e. "Hwabyung"
, and please understand that it is never racism and sneers to Koreans.
A great majority of researchers in South Korea make a pretext of that old Koreans indicates high suicide rate compared with adolescents
as for why suicide rate in South Korea is the highest in the world.However, in part due to deliberately focus on suicide rate, i think that the essence that Koreans carry inherent variants
of MDD(major depressive disease) deliberately have been overlooked.
It is
a complete and scientific fact and is beyond all doubts that the Koreans carry numerous brain-related variants inherent to the Koreans which might be the cause of
The Koreans specific mental disorder i.e. "Hwabyung"
, and please understand that it is never racism and sneers to Koreans.
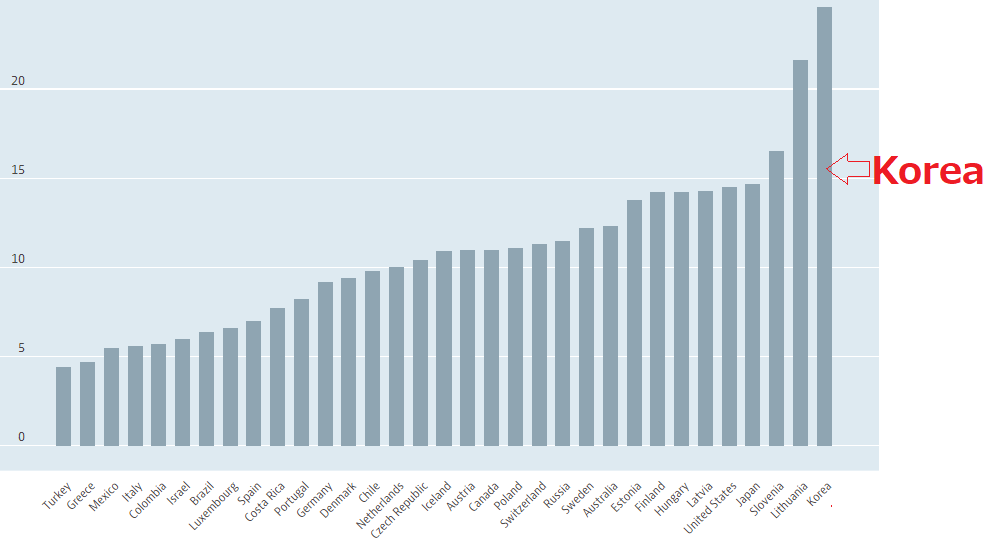
The exact investigation by OECD clearly indicates the fact of The Koreans intellectual ability
 A great majority of Koreans have a daydream that "we are an
excellent ethnic group", therefore, Koreans explicitly show
contemptuous attitudes that "stupid people like Southeast Asia's
people should be obedient to excellent people like Koreans". As the
natural result, Southeast Asia's people who frequently and dairy
contact with Koreans hate Koreans except for K-POP fans who aren't in
daily contact.
A great majority of Koreans have a daydream that "we are an
excellent ethnic group", therefore, Koreans explicitly show
contemptuous attitudes that "stupid people like Southeast Asia's
people should be obedient to excellent people like Koreans". As the
natural result, Southeast Asia's people who frequently and dairy
contact with Koreans hate Koreans except for K-POP fans who aren't in
daily contact.However, there is the following clear data in "Survey of Adult Skills (PIAAC)" by OECD (The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development ) !

 I guess that the data above is the definite evidence of The
Koreans inherent DNA, and needless to say,
it's the exceptional case that The Koreans win internationally
famous science-related awards.
I guess that the data above is the definite evidence of The
Koreans inherent DNA, and needless to say,
it's the exceptional case that The Koreans win internationally
famous science-related awards. To Thailanders, Vietnamese, and Filipino
I think that you, Southeast Asians should know the above fact about intellectual ability of The Koreans.
Abnormal obsession to cosmetic surgery
 I don't know cosmetic surgery expenditure of K-POP stars, but it
is beyond all doubts that all K-POP stars did plastic surgery, so I think
that K-POP stars embody the Lookism (=Appearance Supremacy) in South
Korea.
I don't know cosmetic surgery expenditure of K-POP stars, but it
is beyond all doubts that all K-POP stars did plastic surgery, so I think
that K-POP stars embody the Lookism (=Appearance Supremacy) in South
Korea.Please confirm that "all women are same jawline".

Gender, Globalizationand Aesthetic Surgeryin South Korea
Ruth Holliday(proffessor in University of Leed and Joanna Elfving-Hwang Curtin University
May 2012
This article explores the unusually high levels of cosmetic surgery in South Korea – for both women and men. South Korean’ alleged ‘obsession’ with cosmetic surgery regularly hits headlines both in Asia and the ‘West’ because of its reportedly high take-up rate by both women and men. Cosmetic surgery and skin treatment clinics are now commonplacein urban shopping malls, viewed much like nail and beauty salons in the UK, and providing procedures such as laser removal ofblemishes to 'walk-in’ customers.
Virtually, no winners of famous scientific prizes
 As the results of my investigation about internationally famous
science-related awards including Novel prizes, I found that Koreans
winners are exceptional cases in spite of large population size and
high education rebel.
As the results of my investigation about internationally famous
science-related awards including Novel prizes, I found that Koreans
winners are exceptional cases in spite of large population size and
high education rebel.| result in 2024 | South Korea | Japan | Taiwan |
| prizes winner | 1 | at least over 211 | 13 |
| population size (ratio:South Korea=1.0) |
1.0 | 2.5 | 0.5 |
 I conducted two investigations, first in 2018 and
second in 2024, and there are no award winners in the first investigation, afterward, i found that there is only one The Koreans award winner in 2023 in the second investigation as the above, the
first result is as follows.
I conducted two investigations, first in 2018 and
second in 2024, and there are no award winners in the first investigation, afterward, i found that there is only one The Koreans award winner in 2023 in the second investigation as the above, the
first result is as follows.| result in 2018 | South Korea | Japan | Taiwan |
| prizes winner | 0 | at least over 195 | 11 |
Terrible things about north korea
from Google AI at 6/1/2025
 North Korea is involved in various illegal activities, the above image linked to
"National Geographic" (YouTube).
North Korea is involved in various illegal activities, the above image linked to
"National Geographic" (YouTube).To my regret, Google AI has made a crucial mistake because it doesn't include "North Korean abductions of Japanese citizens"
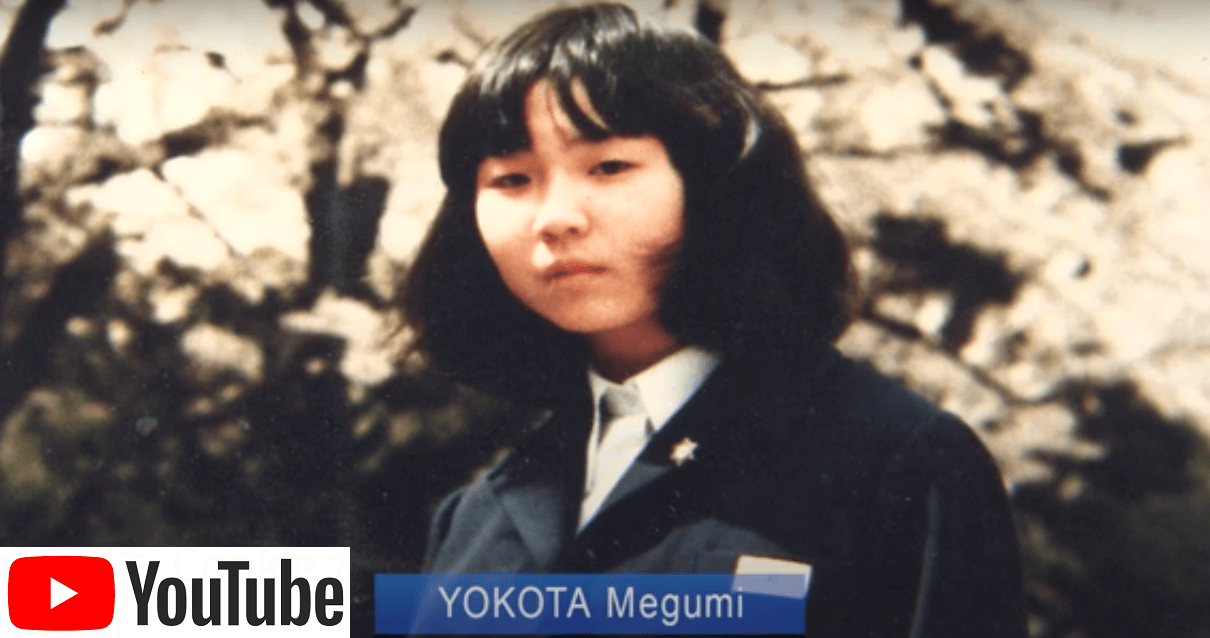
 DNA analysis of the remains sent to Japan by the North Korean government as the remains of Ms. Megumi Yokota showed that
it isn't the remains of Ms. Megumi Yokota.
DNA analysis of the remains sent to Japan by the North Korean government as the remains of Ms. Megumi Yokota showed that
it isn't the remains of Ms. Megumi Yokota.

 original in TickTok (Many Thanks)
original in TickTok (Many Thanks)
 The short footage bellow is a cult-like and shocking performance has
played in front of foreigners, the strange performance strongly implies
"missile worship" in North Korea.
The short footage bellow is a cult-like and shocking performance has
played in front of foreigners, the strange performance strongly implies
"missile worship" in North Korea. Although the relationship the various strange phenomena at the Korean Peninsula and their DNA might be elucidated within next one hundred years, there is no doubt that population genetics papers which indisputably indicate the peculiarity of The Korean DNA have been published.
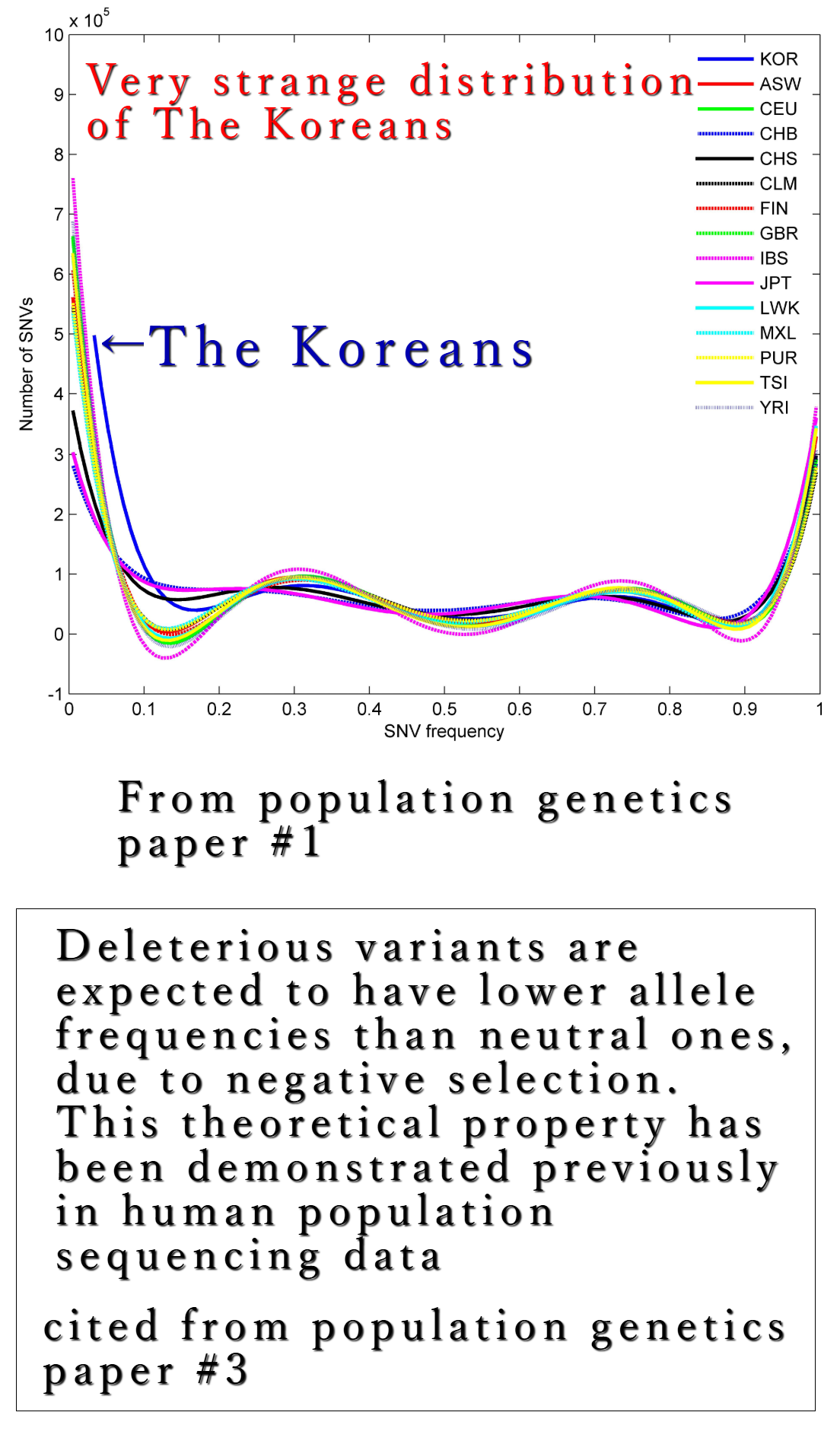
From population genetics paper
According to several population genetics papers, it is beyond all doubts that the genetic structure of Koreans is astonishingly unique and strange.Please visit for details of paper#1.
Koreans have high percentages of non-synonymous variants compared with other ethnic population (the Japanese, the Chinese etc)
A subset of the nsSNPs showed remarkably high allele frequencies among the Koreans studied compared to other populations, including Europeans and west Africans represented in the HapMap project.
In contrast with the SNVs common to other populations in HapMap and 1KGP, the Korean only SNVs had high percentages of non-silent variants, emphasizing the unique roles of these Korean only SNVs in the Korean population.
The portion of non-synonymous SNVs in the ‘1000GP rare’ class was more than twice what was observed in the other classes.
It is possible that these patterns are associated with purifying selection to rapidly remove deleterious alleles in the population
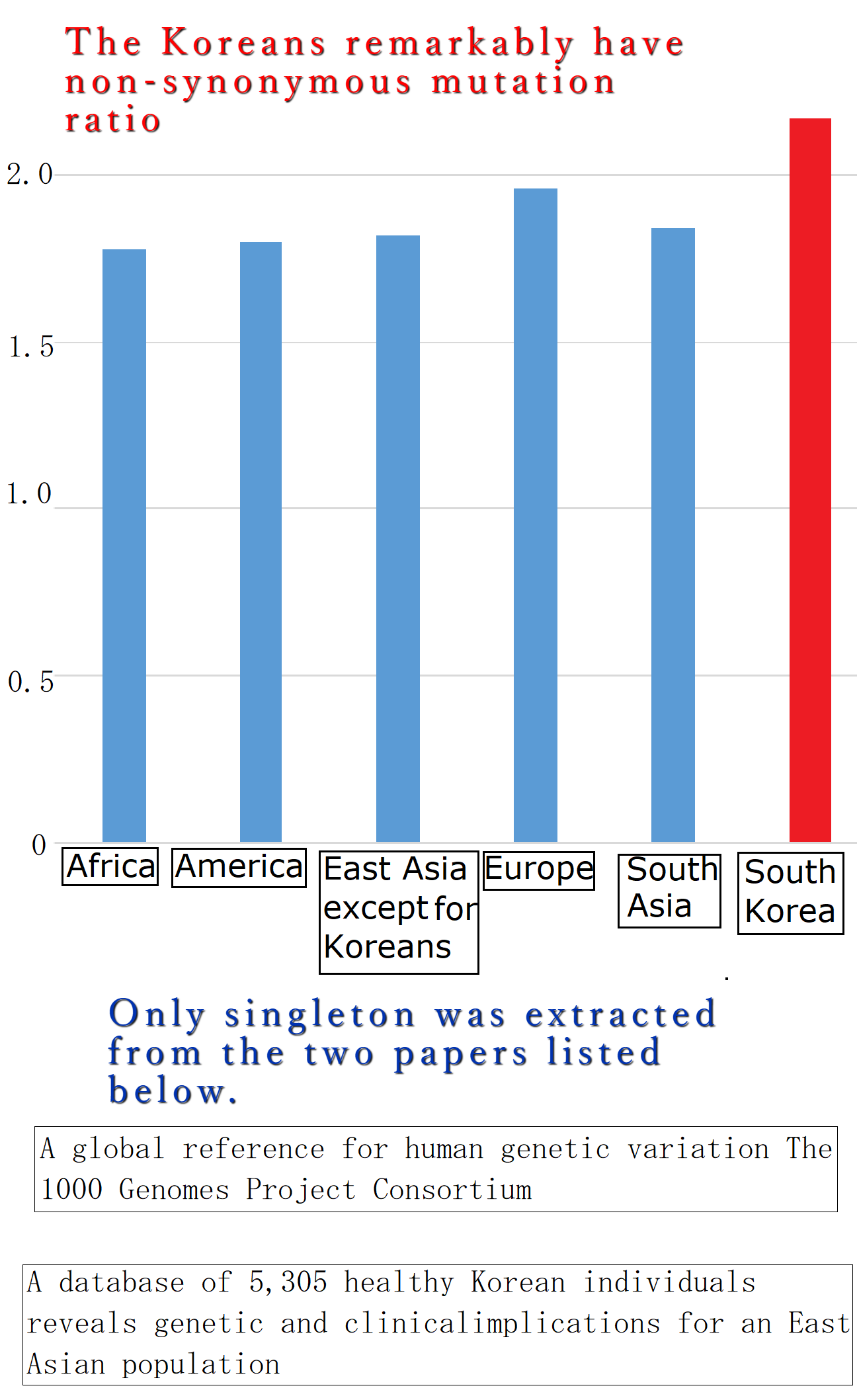
 The above fact means that The Koreans carry more deleterious mutations compared with other ethnic groups. By the strangest chance, South Korea record the lowest birth rate and the highest suicide rate
in the world as above.
The above fact means that The Koreans carry more deleterious mutations compared with other ethnic groups. By the strangest chance, South Korea record the lowest birth rate and the highest suicide rate
in the world as above.As opposed to the other ethnic population, mutations which are inherent to The Koreans extremely biased to some of The Koreans.
Figure 2b shows that nearly 60.59 % (735,271) of Korean only SNVs are observed in only one individual, while 1.04% (12,640) of Korean only SNVs are observed in all 35 individuals. Therefore, we rationally conjectured that Korean only SNVs prevalent across many of the individuals would be more important for treating Koreans differently from other populations in the personalized medicine.
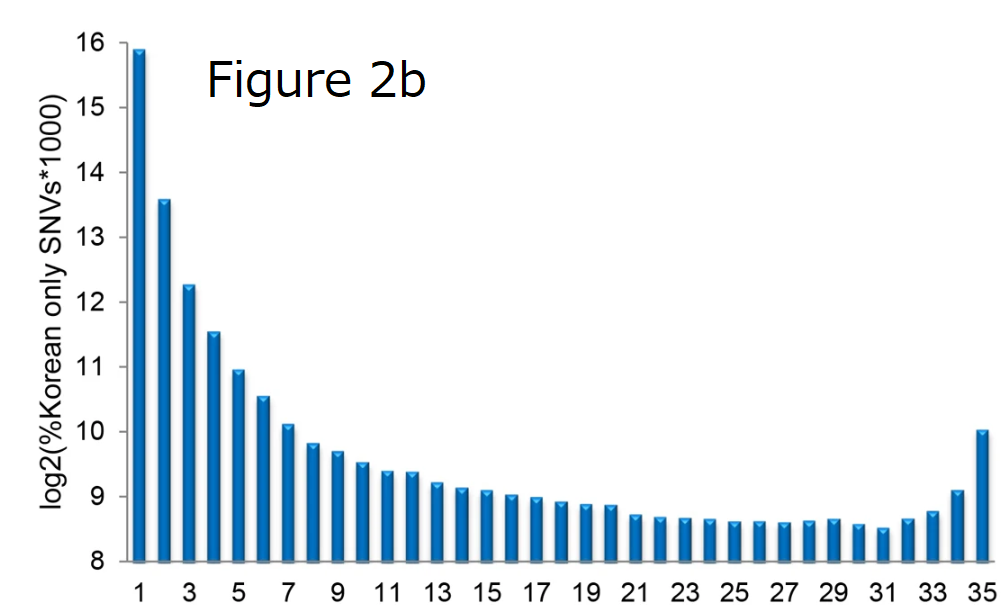
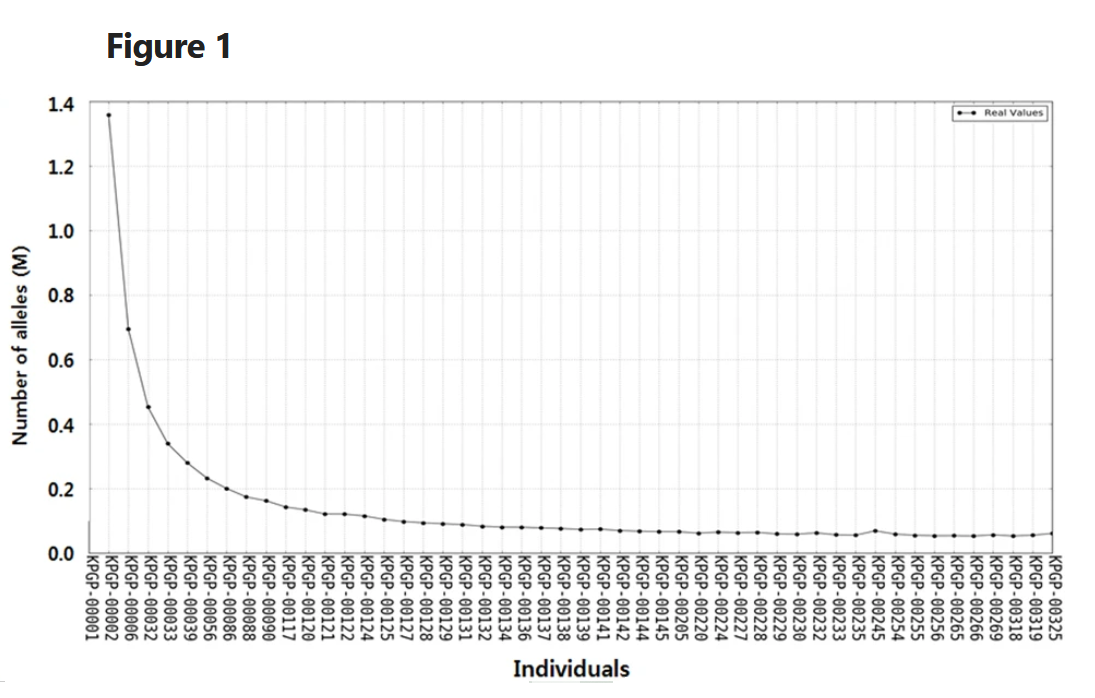
 Although it's a small sample size, two population genetics paper clearly indicates the fact that Korean-specific mutations extremely biased some (about 8%) of The Koreans,
Although it's a small sample size, two population genetics paper clearly indicates the fact that Korean-specific mutations extremely biased some (about 8%) of The Koreans,
 The fact that certain mutations inherent to Koreans is extremely biased
some (about 8%) Koreans, when considered in conjunction with the separate fact that these mutations occur in genes related to human mental health, strongly suggests that Koreans may have a higher proportion of mentally
"insane individuals" than other ethnic groups. However, “insane individuals” does not mean that they have some kind of mental
disease, but simply that they are unusual in terms of their mental state.
The fact that certain mutations inherent to Koreans is extremely biased
some (about 8%) Koreans, when considered in conjunction with the separate fact that these mutations occur in genes related to human mental health, strongly suggests that Koreans may have a higher proportion of mentally
"insane individuals" than other ethnic groups. However, “insane individuals” does not mean that they have some kind of mental
disease, but simply that they are unusual in terms of their mental state.MAF(minor allele frequency) clearly differs from the other ethnic population, including the Japanese, the Chinese.
The variants distribution of Koreans completely differs from The Japanese in spite of same East Asians, and needless to say, differs from other populations too, please see below cited contents.12859_2014_6653_MOESM5_ESM.jpg from population genetics paper #1
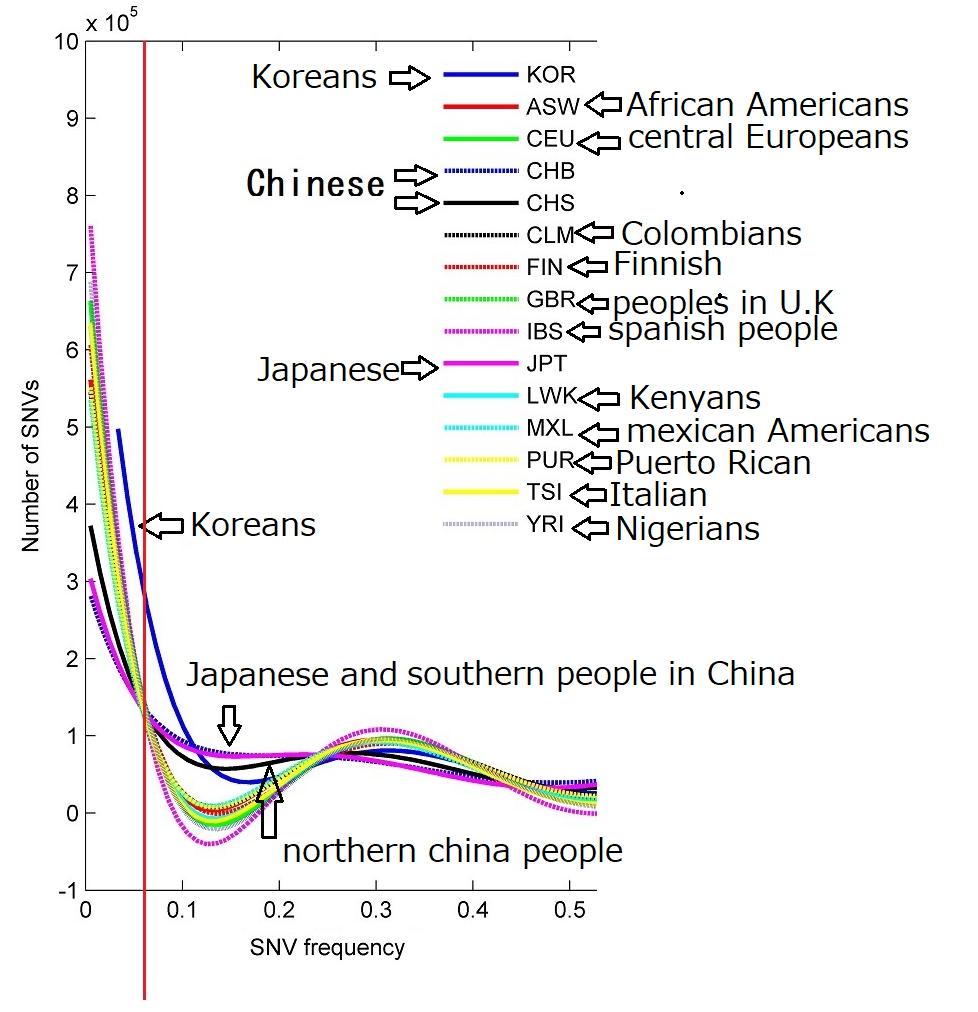
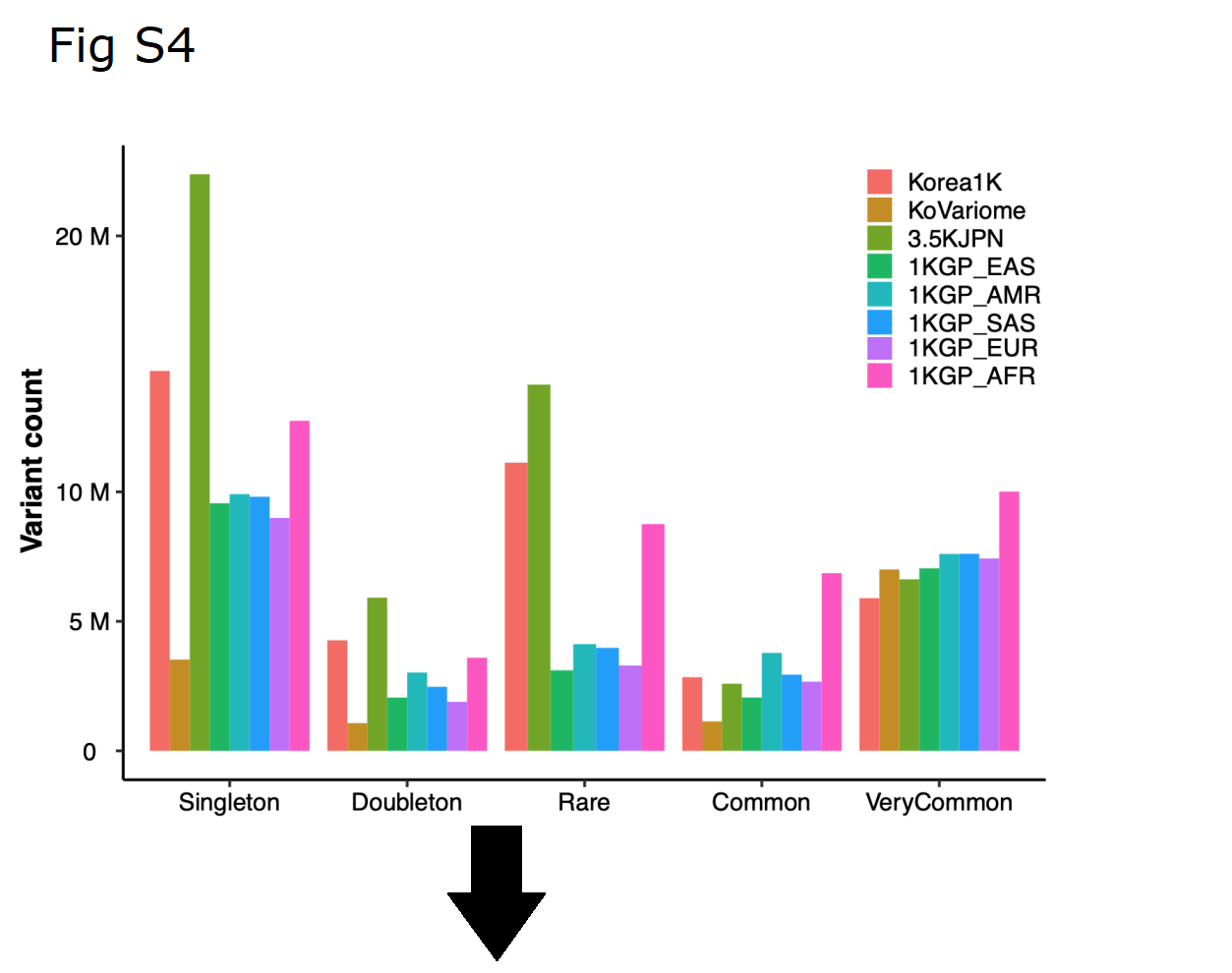
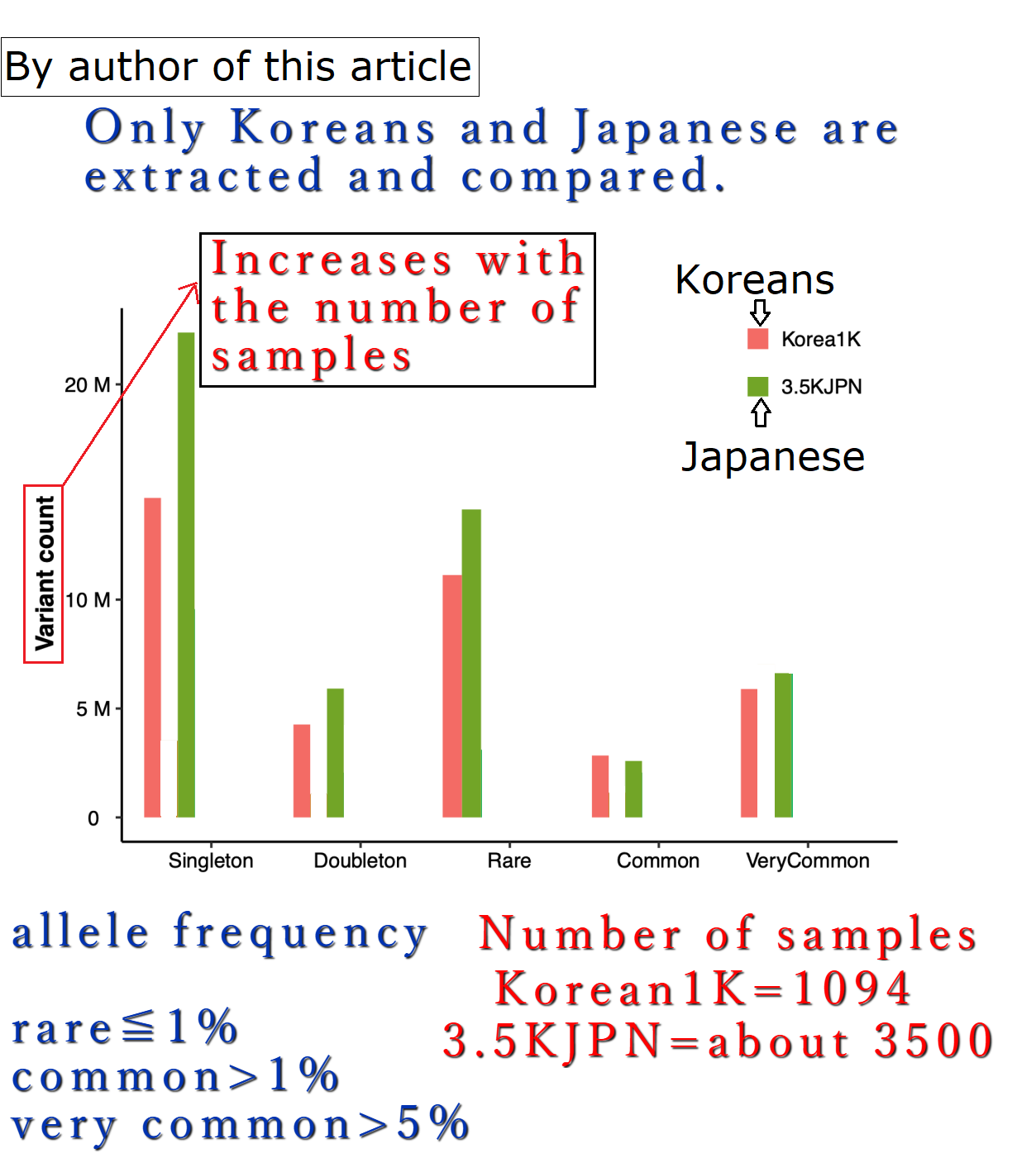
Surprisingly, however, roughly half of the variants in ‘1000GP low frequency’ were classified as ‘frequent in KoVariome’.
Despite their close geographic proximity, the Korean population was shown to be genetically distinct from the Chinese and Japanese populations, highlighting the need for a Korean-specific variome to accurately identify rare disease variants in this population.
The overwhelming majority of mutations which are inherent to Koreans have in relation to mental diseases, personality disorders and human mentality.
List of genes in which there are genetic mutations(=variants) peculiar to Koreans extracted from paper #1 and search results by gene name at NCBI(National Center for Biotechnology Information in USA) is as follows.
Please visit for details.
SNV-1 means number of Koreans inherent mutation in paper #1
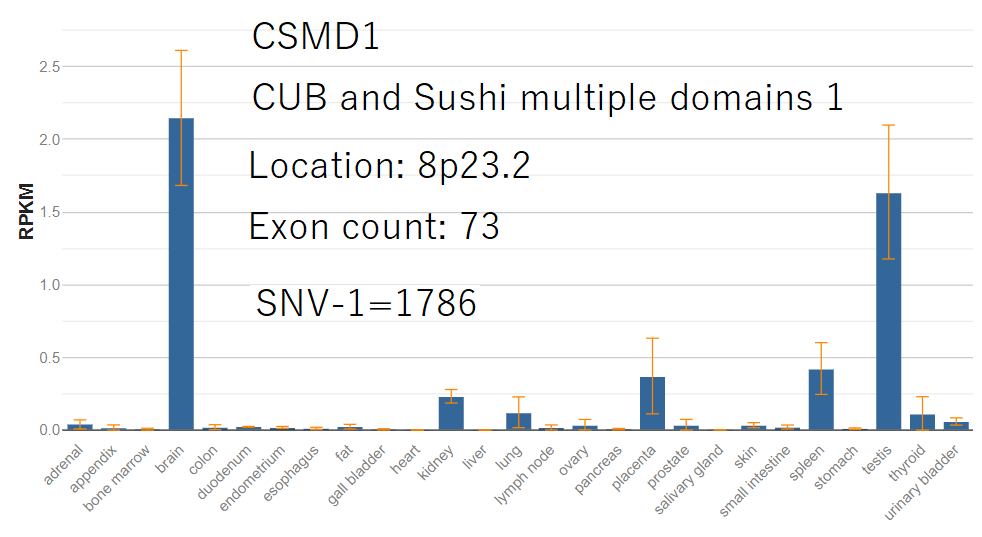
 Please note that the above genetic facts that Korean inherent mutations are clearly related to human brain coincides with the fact that
almost no one Koreans have a few winners of internationally renowned science-related awards, including the Nobel Prize.
Please note that the above genetic facts that Korean inherent mutations are clearly related to human brain coincides with the fact that
almost no one Koreans have a few winners of internationally renowned science-related awards, including the Nobel Prize. Secondly, please know the fact that the vast majority of Koreans
inherent variants(=mutation) are mental disease susceptibility genes, according
to my investigation.
Secondly, please know the fact that the vast majority of Koreans
inherent variants(=mutation) are mental disease susceptibility genes, according
to my investigation.again, Please visit for details.
 From Google AI answer at 6/4/2024
From Google AI answer at 6/4/2024
Name: Kazuo Ueda (researcher of Korean history)
Country: Japan
 I think that we human being should not deny scientific fact, under the name of racism.
As a matter of fact, the ironic thing is that the most racist country in East Asia surely is South Korea, maybe you can't find a Korean female formally married with Blacks.
In the event that you find a Korean female formally married with Blacks, please teach me, to my knowledge, it's very little compared with The Japanese and The Chinese.
I think that we human being should not deny scientific fact, under the name of racism.
As a matter of fact, the ironic thing is that the most racist country in East Asia surely is South Korea, maybe you can't find a Korean female formally married with Blacks.
In the event that you find a Korean female formally married with Blacks, please teach me, to my knowledge, it's very little compared with The Japanese and The Chinese. I infer that the interaction between Koreans DNA (I. e. genetic factors) and the
environment (I. e. sociocultural factors) created two very unique societies
in Korean peninsula.
I infer that the interaction between Koreans DNA (I. e. genetic factors) and the
environment (I. e. sociocultural factors) created two very unique societies
in Korean peninsula. As for genetic factors, Please visit and for details.
As for sociocultural factors, Please visit for details.
 Researcher of population genetics around the world except for Koreans should read the following paper and analyze the very unique genetic architecture of
Koreans DNA like FDA (Division of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics, National Center for Toxicological Research, U.S. Food and Drug Administration).
Researcher of population genetics around the world except for Koreans should read the following paper and analyze the very unique genetic architecture of
Koreans DNA like FDA (Division of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics, National Center for Toxicological Research, U.S. Food and Drug Administration).population genetics paper #1 (FDA)
number of sample:35
Whole genome sequencing of 35 individuals provides insights into the genetic structure of Korean population
Wenqian Zhang et al.
Published: 21 October 2014
The following content is the "meta tag" for the website where the above paper is posted, in other word, the above paper was written by Division of Bioinformatics and Biostatistics, National Center for Toxicological Research, U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Jefferson, USA

In contrast with the SNVs common to other populations in HapMap and 1KGP, the Korean only SNVs had high percentages of non-silent variants, emphasizing the unique roles of these Korean only SNVs in the Korean population.
Specifically, we identified 8,361 non-synonymous Korean only SNVs, of which 58 SNVs existed in all 35 Korean individuals.
Based on our analysis, we hypothesize that Koreans might have different responses to the above mentioned terms-related drugs, when compared to other populations.
Therefore, we rationally conjectured that Korean only SNVs prevalent across many of the individuals would be more important for treating Koreans differently from other populations in the personalized medicine.
Therefore, we inferred that special attention should be made for the Korean population when treated for the above mentioned terms related diseases, since other populations did not carry those Korean only SNVs.
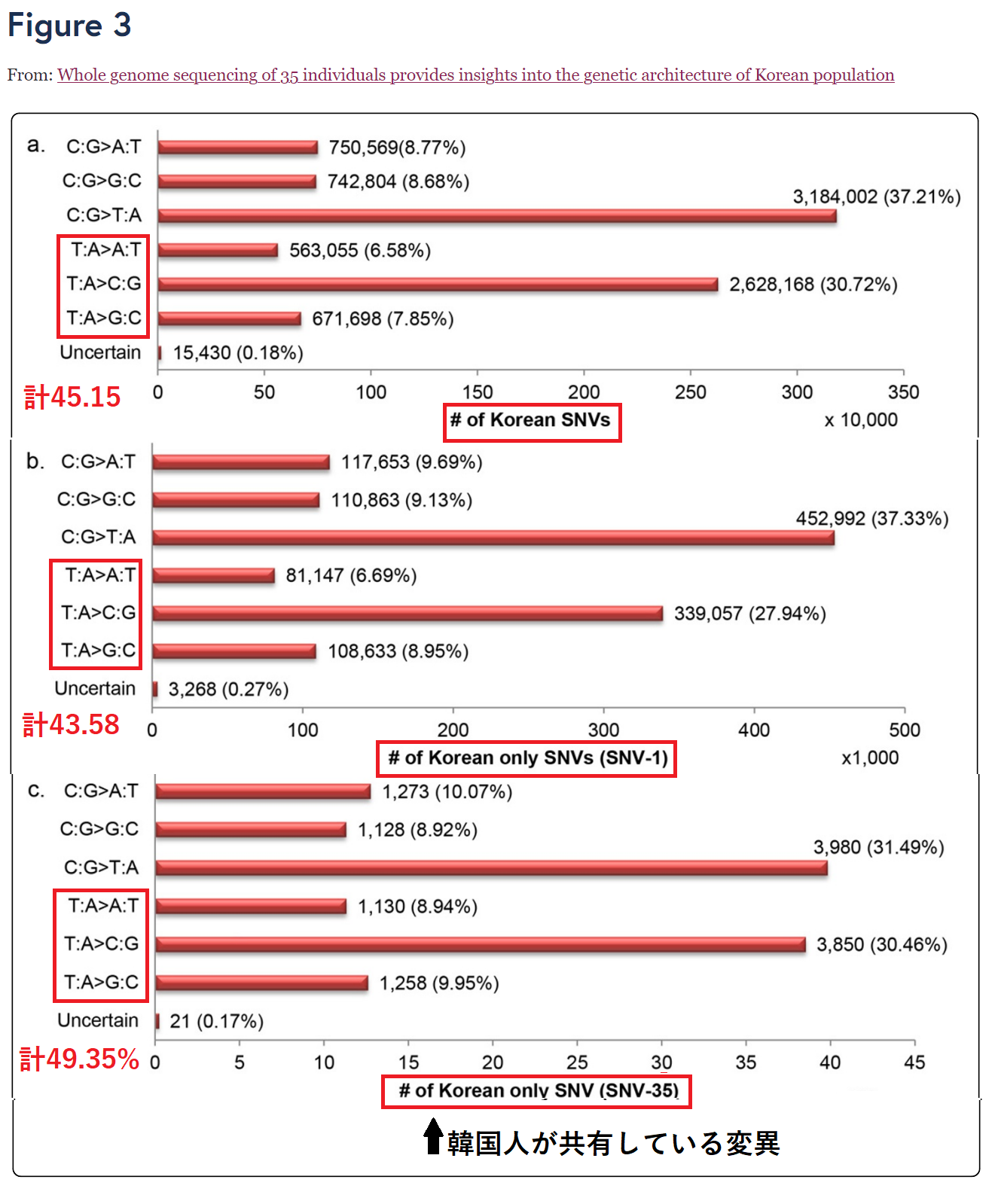
According to the SNV compositions (Figure 3), we found that the most prevalent changes in all three SNV sets was C:G->T:A transition, the same trend as the raw base substitution mutational spectrum in humans [42]. In addition, we found that Korean SNVs and SNV-1 occurred more frequently at C/G base pairs, which was consistent with previous findings [42]. Nevertheless, almost half of SNV-35 mutations occurred at T/A base pairs.
Population genetics paper #2
number of sample:18
Extensive genomic and transcriptional diversity identifiedthrough massively parallel DNA and RNA sequencing of eighteen Korean individuals
Young Seok Ju et.al
2011
A subset of the nsSNPs showed remarkably high allele frequencies among the Koreans studied compared to other populations, including Europeans and west Africans represented in the HapMap project.
We found a subset of genes to be highly enriched for nsSNPs, here called super nsSNP genes
Population genetics paper #3
number of sample:60706
Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans
Monkol Lek et.al
Nature 17 August 2016
Deleterious variants are expected to have lower allele frequencies than neutral ones, due to negative selection. This theoretical property has been demonstrated previously in human population sequencing data12,13 and here (Fig. 1d, e).
population genetics paper #4
number of sample:50
Korean National Standard Reference Variome database of whole genomes with comprehensive SNV, indel, CNV, and SV analyses
Nature Published: 04 April 2018
Jungeun Kim et.al
Surprisingly, however, roughly half of the variants in ‘1000GP low frequency’ were classified as ‘frequent in KoVariome’.
Despite their close geographic proximity, the Korean population was shown to be genetically distinct from the Chinese and Japanese populations, highlighting the need for a Korean-specific variome to accurately identify rare disease variants in this population.
Population genetics paper #5
number of sample:1094
Korean Genome Project: 1094 Korean personal genomes with clinical information
Science Advances 27 May 2020
Sungwon Jeon et.al
Believe it or not, that is the fact.
South Korea has recorded the world's lowest birth rate and the world's highest suicide rate, and North Korea (=Kim dynasty) is the largest absolute monarchy in the world.
Figuratively speaking, South Korea might be "huge mental hospital", and North Korea may be "huge POW camp".